Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, and Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. It is a metabolic disorder in which the body cannot properly use or produce insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. If not treated properly, type 2 diabetes can cause severe health complications. This article will discuss the symptoms, causes, prevention and treatments of type 2 diabetes.
Introduction
Diabetes is a condition which affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes is a common form of diabetes that can develop over time due to various factors, including lifestyle and genetics. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment of type 2 diabetes and strategies for managing and preventing this condition.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?

Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin or when the insulin produced is not effective in regulating blood glucose levels. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps the body to convert glucose from food into energy. When insulin production is impaired, glucose accumulates in the blood, leading to hyperglycemia.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
The exact causes of type 2 diabetes is unknown, but several factors can increase a person’s risk of developing the condition. These include:
- Genetics: Family history plays a vital role in developing type 2 diabetes. People with a parent or sibling who has type 2 diabetes are at higher risk of developing the condition themselves.
- Lifestyle factors: Being overweight, physically inactive, and having an unhealthy diet can all contribute to developing type 2 diabetes.
- Age: As people age, their risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases. This may be because of a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can increase a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes

In addition to the causes mentioned above, several risk factors can increase a person’s likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. These include:
- Age: The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases with age.
- Family history: If someone has a parent or sibling with type 2 diabetes increases the risk of developing the condition.
- Ethnicity: People of certain ethnicities, including African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asian Americans, are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Overweightness or obesity: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
- Inactivity: Physical inactivity is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, as it can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Gestational diabetes: Women who develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at higher risk of developing
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes

The common symptoms of type 2 diabetes can be mild at first, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all. However, as the condition progresses, symptoms may become more severe. Some of the most common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include:
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores or cuts
- Numbness or tingles in the feet or hands
- Recurring infections, such as urinary tract infections or yeast infections
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes

To diagnose type 2 diabetes, your doctor will likely perform a blood test to measure your blood sugar levels. This may involve a fasting blood glucose test, which measures your blood sugar levels after you have fasted for at least eight hours, or a random blood glucose test, which measures your blood sugar levels at any time of day.
If your blood sugar levels are high, your doctor may order additional tests to confirm a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes

Type 2 diabetes may be delayed or prevented through lifestyle changes and healthy habits, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a healthy and balanced diet that is low in sugar, fat, and salt
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Quitting smoking
- Getting enough sleep
- Managing stress
Management of Type 2 Diabetes

Type 2 diabetes can be managed through medication, lifestyle changes, and monitoring blood glucose levels. Some of the medications used to treat type 2 diabetes include:
- Metformin
- Sulfonylureas
- DPP-4 inhibitors
- GLP-1 receptor agonists
- SGLT2 inhibitors
- Insulin therapy
Lifestyle changes that can help you deal with type 2 diabetes include:
- Following a healthy diet
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Monitoring blood glucose levels
- Quitting smoking
- Managing stress
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
If type 2 diabetes isn’t treated or isn’t taken care of well, it can lead to major problems like:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Kidney damage (nephropathy)
- Eye damage (retinopathy)
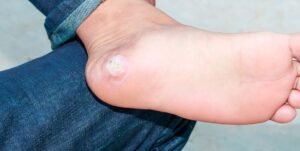
- Foot damage (diabetic foot)
- Skin and mouth conditions
- Hearing impairment
- Alzheimer’s disease
Living with Type 2 Diabetes
If you have type 2 diabetes, dealing with your blood sugar levels and taking steps to prevent and treat complications is essential. This may involve making lifestyle changes, taking medications, and monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly.
It is also essential to work closely with your healthcare team, which may include your primary care physician, endocrinologist, and registered dietitian.
Diet and Exercise for Type 2 Diabetes

A healthy diet and regular workouts can help manage blood sugar levels and improve overall health for people with type 2 diabetes. A healthy and balanced diet for people with type 2 diabetes should include the following:
- Whole grains
- Fruits and vegetables
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
- Low-fat dairy products
In addition to following a healthy diet, regular exercise can help manage blood sugar levels and improve overall health. It is recommended that people with type 2 diabetes engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
Medications for Type 2 Diabetes

Several medications are available to help manage blood sugar levels for people with type 2 diabetes. These include:
- Metformin: This medication reduces the amount of glucose the liver produces and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: These medications stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
- DPP-4 inhibitors: These medications slow the breakdown of incretin hormones, stimulating insulin release and reducing glucose production.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: These medications stimulate insulin production and reduce glucose production.
- SGLT2 inhibitors: These medications work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose by the kidneys, causing it to be excreted in the urine.
- Insulin: In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels.
Working with your healthcare team to determine the best medication regimen for your needs is important.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels

Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly is essential for people with type 2 diabetes. This can be done using a blood glucose meter, which measures the amount of glucose in a small blood sample.
Your healthcare team may recommend different target ranges for blood sugar levels depending on age, overall health, and other medical conditions.
Support for People with Type 2 Diabetes
Living with this type of diabetes can be challenging, and it is important to have a support system in place. This may include family members, friends, healthcare professionals, and support groups.
Several resources are also available for people with type 2 diabetes, including educational materials, online communities, and advocacy organizations.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. While there is no cure for diabetes type 2, several treatment options are available to manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
By making lifestyle changes, taking medications, and working closely with your healthcare team, one can live a healthy and fulfilling life with type 2 diabetes.
FAQs
Can type 2 diabetes be cured?
No, currently, there is no cure for type 2 diabetes. However, it can be managed with lifestyle changes and medications.
What causes type 2 diabetes?
Genetic and lifestyle factors, including obesity, inactivity, and poor diet, usually cause type 2 diabetes.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
Your healthcare team will recommend a target range for your blood sugar levels and how often you should check them. People with type 2 diabetes should check their blood sugar levels at least once daily.
Is it possible to prevent type 2 diabetes?
Yes, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, including maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
Can I still eat my favorite foods with type 2 diabetes?
Yes, you can still enjoy your favorite foods with type 2 diabetes. However, it is important to eat them in moderation and make healthy choices overall. Your healthcare team can help you develop a healthy eating plan that works for you.







0 Comments
Trackbacks/Pingbacks